Cancer is one of the most infamous and dreaded diseases in the world. It is characterised by an abnormal growth of cells that affect different parts of the body. For some cases, it’s treatable but mostly fatal. Worst, it can come without warning and take the life of a loved one or even your own.
Women, in particular, has cervical cancer to be aware of. It is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix – the lower part of the uterus that connects the vagina. Just like most types of cancer, cervical cancer can come with unnoticeable symptoms. You can make assumptions but the only way to know and confirm if you have cervical cancer is by undergoing through a cervical cancer screening.
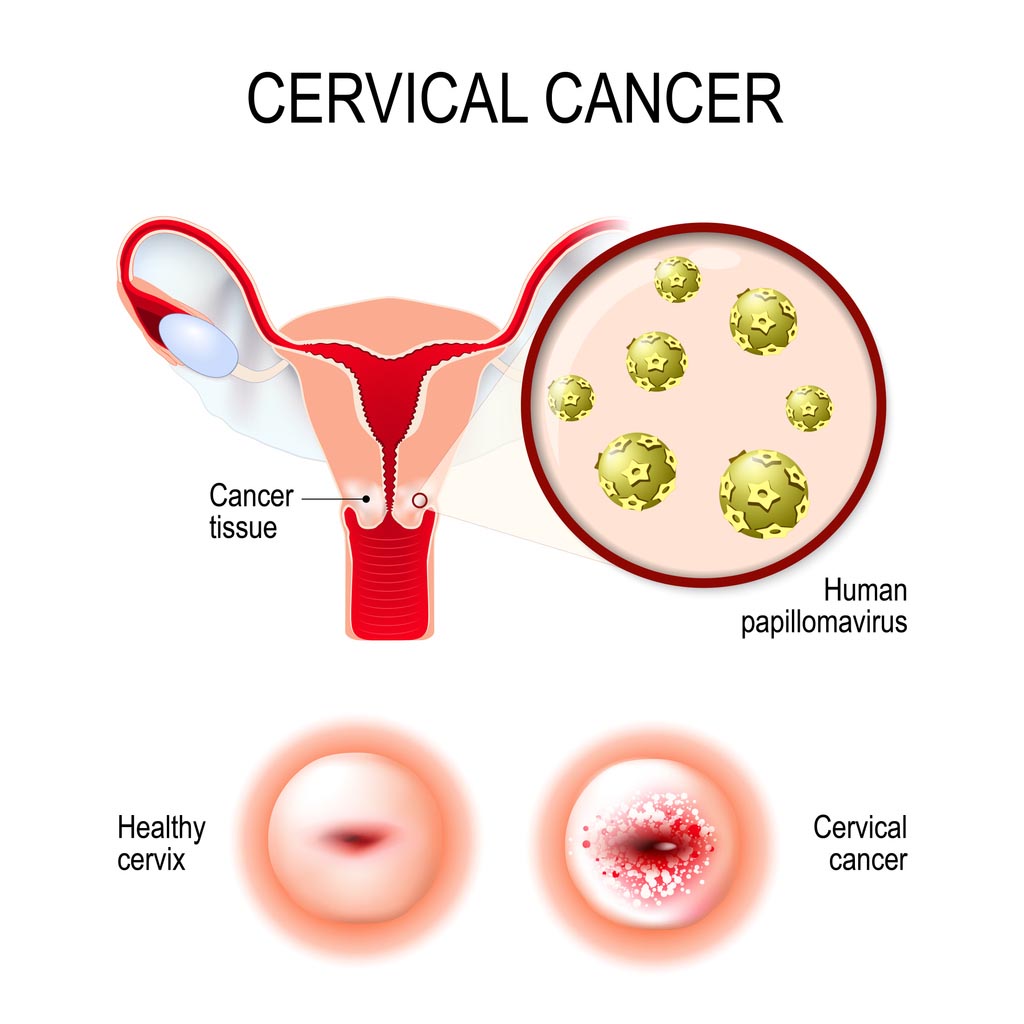
Cervical cancer. vector illustration of the uterus and cervix. Close-up of the Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) that causes diseases. female reproductive system
It is understandable why the majority of women are reluctant or not open to such screening because it could be a bit frightening to get yourself tested for cancer. However, it is important that precautionary measures are taken before cancer can get to you. There are several cervical cancer screening you can take but this article will focus on Papsmear or Pap Test.
What is a Pap smear test?
Pap smear or Paptest, is a procedure to test for cervical cancer. This is done by scraping and collecting cells from the cervix to determine if they have abnormal growth. This is considered effective not only in detecting already developed cervical cancer but also in detecting changes in the cervical cells that may show signs of cancer development. Taking the test does not only help you with the diagnosis but also serves as a precautionary measure toward cervical cancer.
How would I know if need to do a Pap smear?
A pap smear is recommended for women aged 21 and above and can be taken three times (3x) a year. This is also highly encouraged for women with higher risks for cervical cancer including:
- HIV positive or have any other STD
- Have undergone chemotherapy, organ transplant, or any similar procedure that weakens the immune system
- Have History of Smoking
According to DB Clinic, it is advisable, especially for women aged 30-65, to complement pap smear with HPV screening since HPV (human papillomavirus) is one of the main causes of cervical cancer.
Women who are 65 years and older may not be anymore recommended for a pap smear. At the same time, it is also not needed for women who have undergone hysterectomy with removal of the cervix. This is only for women who still have a cervix.
Importantly, Pap smear is not only for women who are sexually active. Though with a lower chance, it is still possible for women who have had not done sexual intercourse to have developed or developing cervical cancer cells.
Who does it and where is it done?
Pap smear testing is usually done by a gynaecologist in his/her clinic. Some general medical check-up already includes this but some don’t. If it is not included in yours, this should be specifically asked from your gynaecologist.
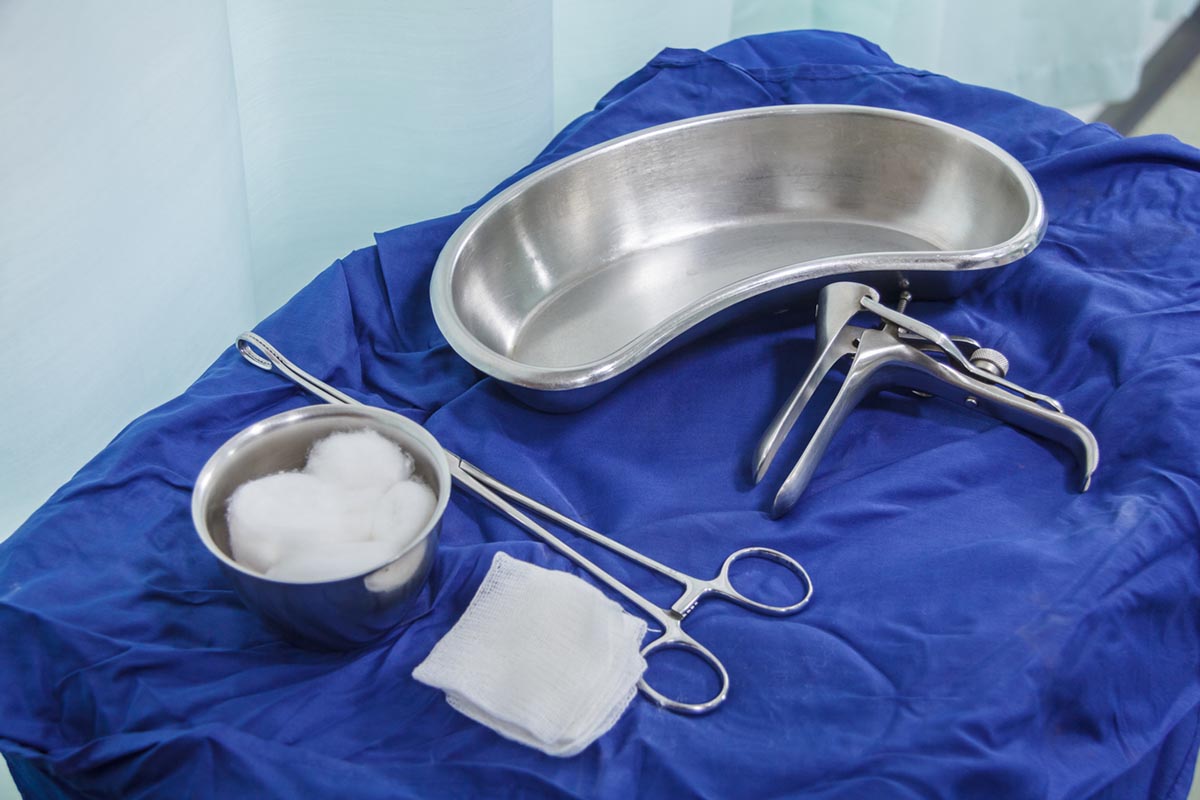
Set Of Smear Test Equipment
What happens during a Pap smear?
First, you will be asked to undress either completely or only waist down. Then you will lie on an examination table with your legs widespread and feet safely placed in stirrups. A metal or plastic tool, called a speculum, will gently be inserted into your vagina. This tool will help in holding and widening your vagina walls so that the doctor can see your cervix. The insertion of the speculum might give you a tingling sensation and some pressure your pelvis.
When the cervix can be clearly seen, the doctor will collect cell samples. The doctor may use any of these tools:
- a spatula
- a soft brush and a spatula
- a cytobrush, a device which is a combination of a spatula and a soft brush
The samples cells will be preserved and sent to the testing laboratory.
You might feel a little discomfort while samples are being scraped. There may also be some light vaginal bleeding but will only be temporary. If bleeding further continues after days from screening, call your doctor.
How long does Pap smear last?
The procedure is very short as it usually just takes 10-20 minutes for your doctor to get sample cells from your cervix.
How should I prepare for the test?
In taking the test, it is important that your body is relaxed as this will hasten the procedure. But aside from being relaxed, here are some few things to take before taking the test:
- Make sure that you are not having your menstrual cycle. This may affect the results making it less accurate.
- Avoid sexual intercourse, douching, or any vaginal repositories at least two days before your pap smear. These activities may make changes to cervical cells, thus, may result in no detection of abnormal growth.
What results can I expect?
The release of the results of your pap smear will depend on your doctor or clinic where you took the test. However, there are two results that you can expect:
- Normal or Negative – If you received this result, it means that no abnormal cell growth was detected. This is actually good news. Your doctor will not recommend any further testing. You may take your next pap smear after three (3) years.
- Abnormal or Positive – Receiving this result does not automatically mean you have cancer. A positive result means that abnormal cells were detected in your cervix. Some could be pre-cancerous, some may not be. Detected abnormal cells may be in these following levels:
- Atypical. The pap smear detects changes in the cells on the surface of the cervix. The test will be re-analysed if there is the presence of any HPV before any further tests will be required.
- Mild
- Moderate
- Severe Dysplasia
- Carcinoma in Situ. This means that cell changes so abnormally that the test confirms cancer is present.
For those levels in which the doctors are not yet sure if cancer is present, further testing will be required. The next steps will only be determined if questions regarding your results are answered and confirmed.
