A multitude of tests is currently available to detect the SARS-CoV-2 infection responsible for COVID-19. The tests have different purposes and therefore not overlapping with each other in terms of reliability and effectiveness.
This article will introduce the various COVID-19 testing solutions: molecular tests, antigen, and antibody. Let’s know more about the subject.
Molecular Tests
The most reliable for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection is the molecular test. It is performed on a sample of the respiratory tract taken through the so-called swab.
The nasal / oral-pharyngeal swab is an examination that consists of the removal of the superficial cells of the mucous membrane. The sampling is carried out with a cotton swab in a few seconds. It is non-invasive neither painful. However, the patient may feel discomfort when the swab comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the nose and oral cavity.
The swab must be performed correctly. It is essential to rely on specialized operators who ensure adequate sample collection. The analysis must be carried out at the regional reference laboratories.
The sample collected is examined in the laboratory. The extraction, purification, and research of the viral RNA (the genome of the SARS-CoV-2 virus) is carried out through the molecular method of real-time RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription- Polymerase Chain Reaction). The laboratory analysis allows identifying the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the material taken with the swab. At this point, confirm or exclude a diagnosis of infection.
Antigen test
Antigen tests examine the surface proteins of the virus (antigens) as opposed to the viral genome in molecular tests.
The sample is always collected through a nasopharyngeal swab, and response times are short (about 15-30 minutes, while for the molecular test, it takes about 24-48 hours). The sensitivity of the antigen tests is lower than those of the molecular test. Those who test positive on the rapid test should undergo the molecular test to confirm the results.
The rapid test was introduced for the screening of passengers in airports and ports. It is also helpful in the school context because it could accelerate the diagnosis of suspected COVID- 19 and simplify case identification, isolation, and contact tracing.
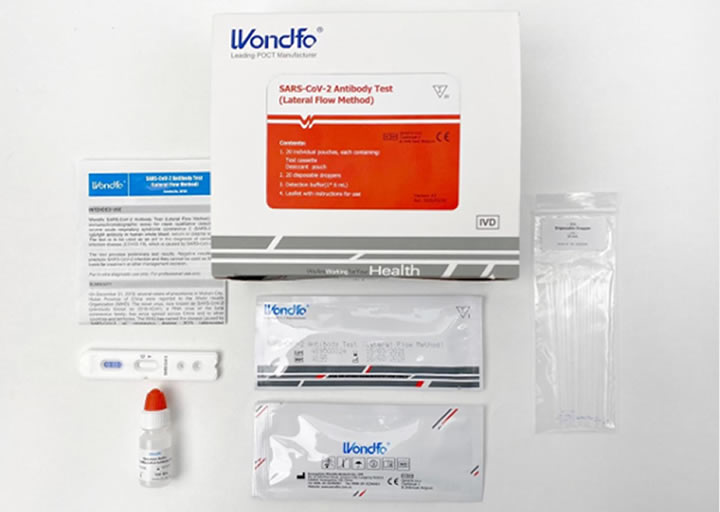
Antibody test
Serological tests are based on the patient’s blood test. They can be rapid (a drop of blood is sufficient) or quantitative (the patient must be subjected to a blood sample).
Rapid or qualitative serological tests make it possible to determine if the subject has contracted the virus and his immune system has produced responding antibodies.
The antibodies involved are IgM immunoglobulins (the first to be produced in case of infection) and IgG (when the level of the former drops). If IgG is detected in the blood sample, it means that the infection occurred in the past. It is not yet clear whether a subject with IgG antibodies is immune.
The serological test highlights the presence of antibodies against the virus and indicates any exposure to SARS-CoV-2. The test is not suitable for detecting infection in progress. Therefore, it cannot replace the molecular test (the swab) to verify a subject’s positivity. This type of test can be helpful in the epidemiological field to estimate the spread of the infection within a community.
Conclusion
It is always suggested to adopt certified and consolidated solutions. For some time, we have heard about Wondfo Biotech tests.
The company offers Covid-19 molecular tests, rapid antigen tests, antibody tests with NMPA, CE, FDA, MDALLT, MDSAP, and WHO POT certifications. The tests can be provided both at point-of-care and home.
To have more information about the ongoing testing situation. Check out the Wondfo website.

